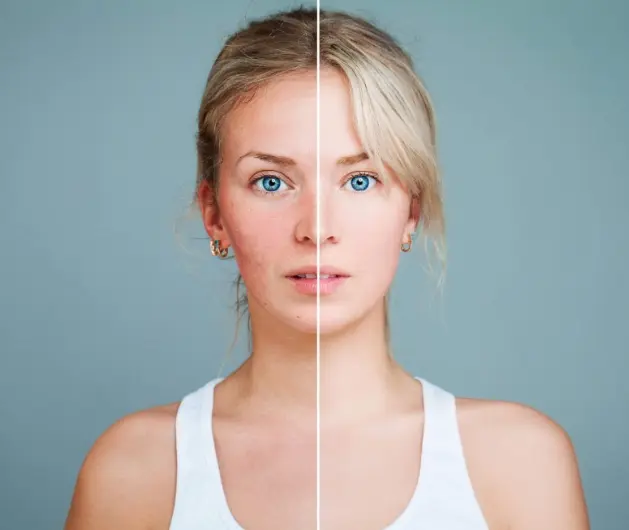
Understanding Rosacea
Before diving into treatment options, it's essential to understand the types and symptoms of rosacea. There are four main subtypes:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea: This type is marked by redness and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Resembling acne, this type includes redness along with bumps and pimples.
- Phymatous Rosacea: This type is characterized by thickened skin and a bumpy texture.
- Ocular Rosacea: Affecting the eyes, this type causes redness, irritation, and swollen eyelids.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against rosacea. These medications are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce redness, inflammation, and bumps.
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a commonly prescribed topical antibiotic that helps reduce inflammation and prevent pustules and papules. It is available in various forms, including creams, gels, and lotions.
Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid helps reduce redness and swelling. It works by preventing the growth of bacteria on the skin and reducing keratin production, which can block pores. Azelaic acid is available in gel and foam formulations.
Ivermectin
Ivermectin targets skin mites that may contribute to rosacea symptoms. It has anti-inflammatory properties and is typically used for more severe cases.
Oral Medications
For moderate to severe rosacea, oral medications may be necessary. These can help reduce inflammation and treat symptoms that topical treatments cannot fully address.
Antibiotics
Oral antibiotics like doxycycline, minocycline, and tetracycline are effective in reducing inflammation and clearing up papules and pustules. These antibiotics are usually prescribed for short-term use to avoid antibiotic resistance.
Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, commonly used to treat severe acne, can also be effective for severe cases of rosacea. It works by reducing oil production in the skin. However, due to its potential side effects, it is generally reserved for the most severe cases.
Laser and Light Therapies
Laser and light therapies can be highly effective in treating the redness and visible blood vessels associated with rosacea. These treatments are usually performed by dermatologists and may require multiple sessions.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy targets and shrinks blood vessels, reducing redness and improving the skin’s appearance. Pulsed dye lasers (PDL) and intense pulsed light (IPL) are commonly used.
Light Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) uses light to activate a photosensitizing agent applied to the skin. This helps reduce inflammation and can improve the overall appearance of the skin.
Lifestyle and Skincare Adjustments
In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle and skincare adjustments can help manage rosacea symptoms.
Identify and Avoid Triggers
Common triggers for rosacea flare-ups include sun exposure, spicy foods, alcohol, hot beverages, and stress. Keeping a diary to track flare-ups can help identify personal triggers, which can then be avoided.
Gentle Skincare
Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products designed for sensitive skin can help prevent irritation. Look for products that are free of alcohol and other harsh ingredients.
Sun Protection
Sun exposure is a significant trigger for many people with rosacea. Wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher can help protect the skin. Additionally, wearing hats and seeking shade can minimize sun exposure.
Consultation with a Dermatologist
It is crucial to consult with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan. A dermatologist can help determine the best combination of treatments based on the type and severity of rosacea.
Conclusion
While there is no cure for rosacea, a variety of treatments can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Topical and oral medications, laser and light therapies, and lifestyle adjustments all play a role in controlling rosacea. Working closely with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan is essential for achieving the best possible outcome. By understanding and managing triggers, using appropriate skincare, and exploring medical treatments, individuals with rosacea can lead healthier, more comfortable lives.