What is Angioedema?
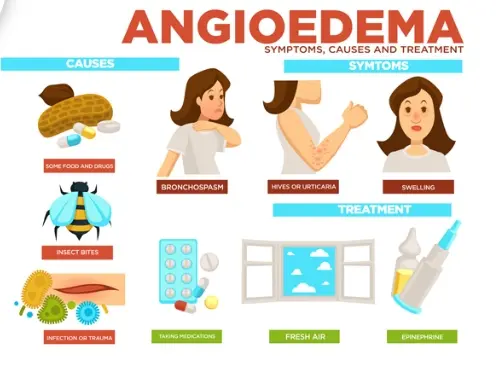
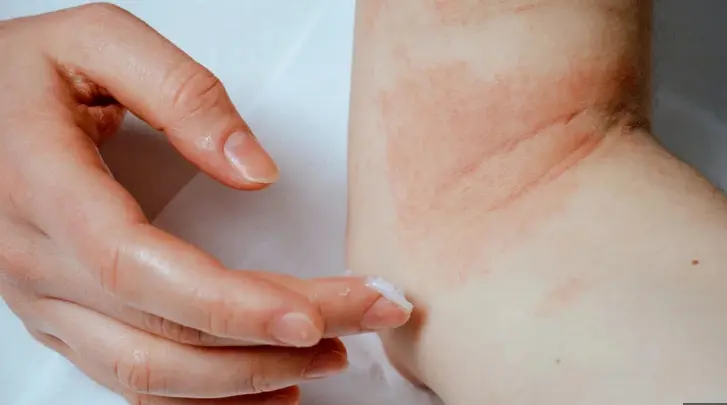
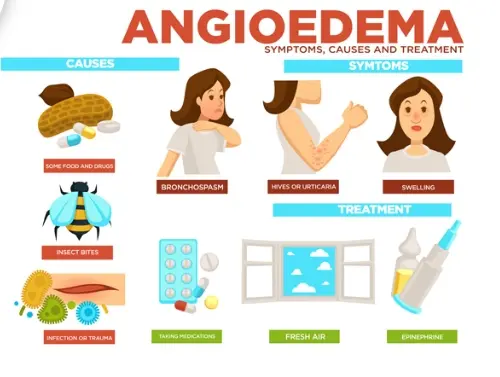
Angioedema is a serious medical condition characterized by sudden swelling of the deep layers of the skin, mucous membranes, and underlying tissues. It can affect various parts of the body, including the face, lips, tongue, throat, and extremities. Angioedema is often associated with an allergic reaction, but it can also be caused by certain medications, such as Rexulti, Xeljanz, and Libtayo.
Angioedema can range from mild to severe and can be life-threatening if it affects the airway. Symptoms typically develop within minutes or hours of exposure to the trigger and may include:
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Difficulty breathing
- Hoarseness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
Medication-Induced Angioedema: What You Need to Know
Certain medications, including Rexulti, Xeljanz, and Libtayo, have been associated with an increased risk of angioedema. These medications belong to different drug classes and are used to treat various medical conditions.
Rexulti (brexpiprazole) is an atypical antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Xeljanz (tofacitinib) is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Libtayo (cemiplimab) is a monoclonal antibody used to treat advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
The exact mechanism by which these medications cause angioedema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to their effects on the immune system and blood vessels. Angioedema associated with these medications can occur at any time during treatment, but it is more common in the first few weeks.
Rexulti, Xeljanz, Libtayo: Risks and Treatment
If you are taking Rexulti, Xeljanz, or Libtayo and experience any symptoms of angioedema, it is crucial to stop taking the medication immediately and seek medical attention.2 Angioedema can be a life-threatening condition, and prompt treatment is essential.
Treatment for angioedema typically involves:
- Discontinuing the medication that caused the reaction
- Administering epinephrine (adrenaline) to reduce swelling and improve breathing
- Providing oxygen therapy
- Administering antihistamines or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Monitoring the patient’s condition and providing supportive care
Learn More About Angioedema
Angioedema is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. If you are experiencing symptoms of angioedema, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. For more information about angioedema, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, refer to credible medical resources such as the National Library of Medicine, the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, or consult with a healthcare professional.